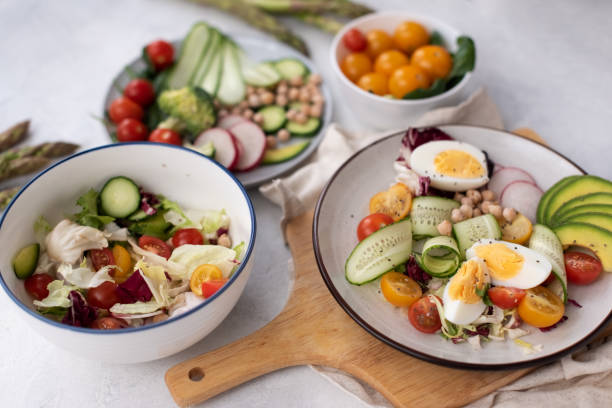
The diet that you adopt is a very important aspect of your health. There are many factors to consider in order to get the best results out of it. You need to focus on foods that are beneficial to your health. These include foods with carbohydrates, Omega-3 fatty acids and added sugars.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are important to your health, and they are found in many foods. It’s important to learn how to choose carbohydrates that are healthy. Your healthcare professional can help you develop a balanced diet. They can also help you determine the proper portion size.
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They are broken down into smaller units of sugar, which are then absorbed by the small intestine. The smaller units of sugar then travel to the liver. From there, they are converted into glucose. Glucose is then used for energy.
You can find carbohydrates in fruits and vegetables, dairy products, and grains. However, you should be cautious about adding carbohydrates to your diet. Some people mistakenly believe that they are fattening.
In the US, most adults should get about 45 to 65 percent of their daily calories from carbohydrates. People with diabetes should limit the amount of carbohydrates they eat.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids that are essential for the health of the human body. They are mostly found in fish, flaxseed, and vegetable oils.
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to lower triglyceride levels and help prevent cardiovascular disease. It also reduces inflammation. Inflammation is an immune response to infection or disease. It also helps in reducing erectile dysfunction. Cenforce 100 and Fildena 100 is the ED treating medicine.
The benefits of omega-3 fatty acids are thought to be related to their ability to improve the function of the endothelium, which is the inner lining of the arteries. By preventing blood platelets from clumping together, these fats can prevent plaque from forming in the arteries, lowering the risk of stroke and heart attack.
The American Heart Association recommends that people consume at least two servings of seafood each week. The primary sources of omega-3s are marine algae, cold-water fish, and fish oil.
Added sugars
Added sugars are commonly added during the manufacturing process of foods. They provide little nutrition or value, and contribute many calories. These empty calories may lead to obesity and other health issues.
Most experts recommend limiting added sugars to no more than 10% of a daily diet. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended a 5% limit on total sugars.
To figure out how much added sugar you’re taking in, you need to know where to look. Besides your meals, you can find added sugars in some desserts, fruit juices, and sodas. For example, a 12-ounce soda can contain 10 teaspoons of sugar.
Added sugars may be associated with metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Although studies on the association between these conditions and added sugars are limited, the link between the two is clear.
Processed foods
While processed foods can be a convenience, they can also be unhealthy. Processed foods are typically high in salt and sugar, which increase the risk of heart disease and cancer. Buying more fruits, vegetables and dairy products is a great way to get more healthy foods into your diet.
Ultra-processed foods (UPFs) are an umbrella term for food that have undergone heavy processing to make them shelf-stable or last longer. Compared to unprocessed foods, they lack key vitamins and minerals, which may contribute to adverse health effects.
Recent studies have found associations between UPFs and a wide range of adverse health outcomes. However, direct causal links between these foods and diseases remain uncertain. Many factors contribute to individual dietary patterns, including socioeconomic status, culture, climate change and geographical location.
Fast food
A diet rich in fast food can be detrimental to your health. It can lead to inflammation, digestive problems, and immune system issues.
Fast food has been linked to various types of cardiovascular conditions, such as heart attack and stroke. It also raises the risk of type 2 diabetes, obesity, and high blood pressure. Eating more fast foods increases your risk of heart disease, and consuming fast food more than twice a week can increase your risk of diabetes.
One study found that people who ate more than two fast foods per day were more likely to have diabetes. Another study found that people who consumed fast foods more often were at greater risk for heart attack.
Many people are concerned about the negative impact of eating fast foods on their health. However, fast food does not have to be harmful. Just as long as you follow the right guidelines, it can be a good choice for your diet.